Tetrachromatic Humans See 100 Times More Colors
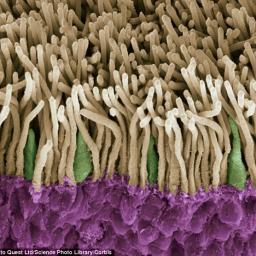 The same genetic mutation that makes people color-blind, can allow a small portion of women to perceive 100 times as many shades of colors as the rest of us, up to a potential 99 million. The mutations, when found on both X-chromosomes, can cause development of a 4th cone cell in a photosensitive layer in the back of the eye that responds to specific wavelengths of light. This increased visual acuity has been found most substantial in mid to long-wavelength, or "reddish", spectral components.
The same genetic mutation that makes people color-blind, can allow a small portion of women to perceive 100 times as many shades of colors as the rest of us, up to a potential 99 million. The mutations, when found on both X-chromosomes, can cause development of a 4th cone cell in a photosensitive layer in the back of the eye that responds to specific wavelengths of light. This increased visual acuity has been found most substantial in mid to long-wavelength, or "reddish", spectral components. Lots of animals are tetrachromats, including birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles and insects, but only a handful of human tetrachromats have been identified since 2012. This increased visual ability does come with a disadvantage of offspring having a high likelihood of color-blindness. Continued research may help scientists find a way to improve the vision of the (much larger) portion of the population that suffers from color-blindness.
More information on scientific studies of human tetrachromacy can be found here.