Process takes COâ‚‚ from the air, converts it to carbon nanotubes
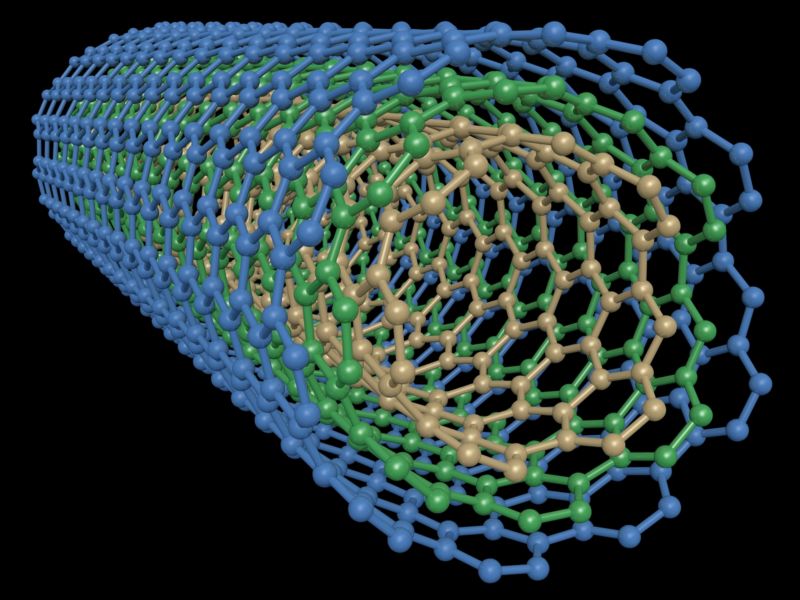
Enlarge / A multi-walled carbon nanotube. (credit: NASA)
Carbon capture and storage involves the separation of carbon dioxide from other gases, after which it's pumped underground for storage. It's likely to be needed to reach our climate goals without simply shutting down many existing fossil fuel plants, and it will be essential if we overshoot our emissions goals by mid-century. But it also adds significant costs to building and operating fossil fuel plants, which explains why the process has never gotten past the point of sporadic demonstration projects.
An alternative to storage involves turning the carbon that's captured into a useful product-something the XPrize has made one of its challenges. Doing so requires two things: overcoming the chemical stability of CO2 and making a product that sells at a profit. We recently stumbled across a bit of creative chemistry that turns carbon dioxide from the air into a product that should be profitable: high-quality carbon nanotubes.
Something in the airOur current methods for making carbon nanotubes typically rely on hydrocarbons. The chemistry of this source helps drive the tube-forming reactions, since it can be energetically favorable to remove the hydrogens from these molecules. Unfortunately, this doesn't get rid of CO2, and it's only good for emissions in the sense that some of the carbon ends up in nanotubes instead of the air.
Read 8 remaining paragraphs | Comments