How Facebook and Google are helping the CDC forecast coronavirus
When it comes to predicting the spread of an infectious disease, it's crucial to understand what Ryan Tibshirani, an associate professor at Carnegie Mellon University, calls the "the pyramid of severity." The bottom of the pyramid is asymptomatic carriers (those who have the infection but feel fine); the next level is symptomatic carriers (those who are feeling ill); then come hospitalizations, critical hospitalizations, and finally deaths.
Every level of the pyramid has a clear relationship to the next: "For example, sadly, it's pretty predictable how many people will die once you know how many people are under critical care," says Tibshirani, who is part of CMU's Delphi research group, one of the best flu-forecasting teams in the US. The goal, therefore, is to have a clear measure of the lower levels of the pyramid, as the foundation for forecasting the higher ones.
But in the US, building such a model is a Herculean task. A lack of testing makes it impossible to assess the number of asymptomatic carriers. The results also don't accurately reflect how many symptomatic carriers there are. Different counties have different testing requirements-some choosing only to test patients who require hospitalization. Test results also often take upwards of a week to return.
The remaining option is to measure symptomatic carriers through a large-scale, self-reported survey. But such an initiative won't work unless it covers a big enough cross section of the entire population. Now the Delphi group, which has been working with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to help it coordinate the national pandemic response, has turned to the largest platforms in the US: Facebook and Google.
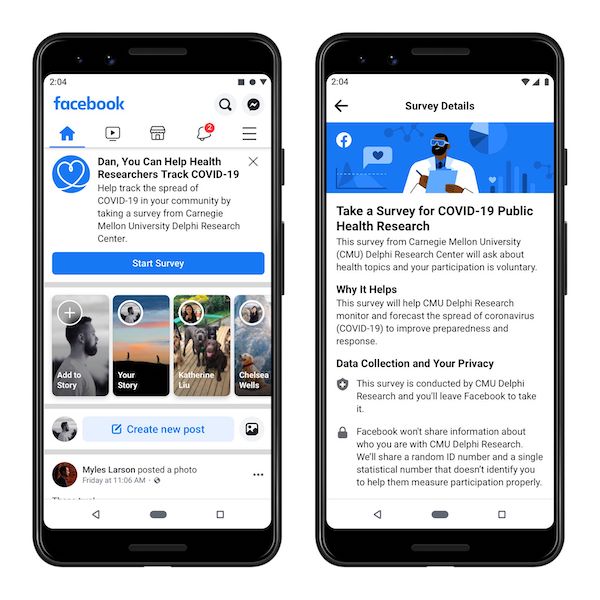
In a new partnership with Delphi, both tech giants have agreed to help gather data from those who voluntarily choose to report whether they're experiencing covid-like symptoms. Facebook will target a fraction of their US users with a CMU-run survey, while Google has thus far been using its Opinion Rewards app, which lets users respond to questions for app store credit. The hope is this new information will allow the lab to produce county-by-county projections that will help policymakers allocate resources more effectively.
Neither company will ever actually see the survey results; they're merely pointing users to the questions administered and processed by the lab. The lab will also never share any of the raw data back to either company. Still, the agreements represent a major deviation from typical data-sharing practices, which could raise privacy concerns. "If this wasn't a pandemic, I don't know that companies would want to take the risk of being associated with or asking directly for such a personal piece of information as health," Tibshirani says.
Without such cooperation, the researchers would've been hard pressed to find the data anywhere else. Several other apps allow users to self-report symptoms, including a popular one in the UK known as the Covid Symptom Tracker that has been downloaded over 1.5 million times. But none of them offer the same systematic and expansive coverage as a Facebook or Google-administered survey, says Tibshirani. He hopes the project will collect millions of responses each week.
Tibshirani doesn't know whether the collaborations with Facebook and Google will last once the pandemic is over. Without the urgency and pressure of the global crisis, he isn't sure the platforms or their users will still be willing to give up such intimate health information. But he and the rest of the lab are grateful for what they are getting now. "I think that this has the potential for enormous impact," he says.