Beta distribution with given mean and variance
It occurred to me recently that a problem I solved numerically years ago could be solved analytically, the problem of determining beta distribution parameters so that the distribution has a specified mean and variance. The calculation turns out to be fairly simple. Maybe someone has done it before.
Problem statementThe beta distribution has two positive parameters, a and b, and has probability density proportional to [1]
for x between 0 and 1.
The mean of a beta(a, b) distribution is
and the variance is
Given and ^2 we want to solve for a and b. In order for the problem to be meaningful must be between 0 and 1, and ^2 must be less than (1-). [2]
As we will see shortly, these two necessary conditions for a solution are also sufficient.
VisualizationGraphically, we want to find the intersection of a line of constant mean
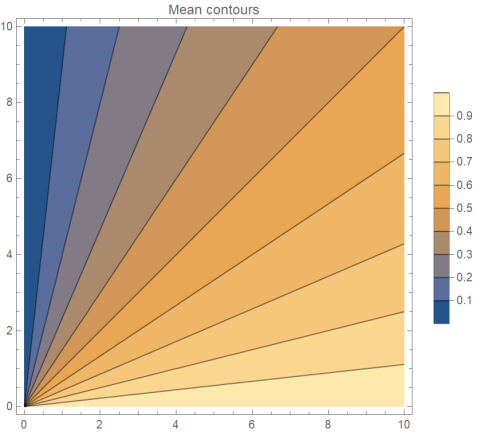
with a line of constant variance.
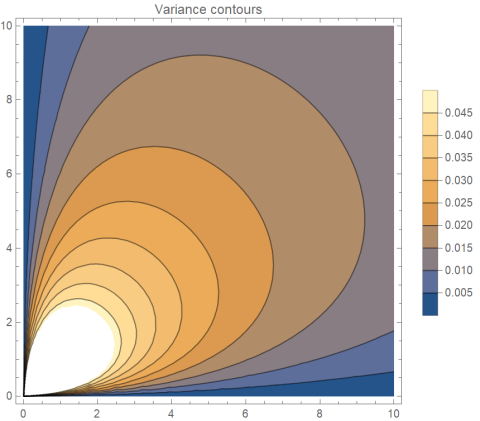
Note that the scales in the two plots differ.
SolutionIf we set
then b = ka and so we can eliminate b from the equation for variance to get
Now since a > 0, we can divide by a^2
and from there solve for a:
and b = ka.
We require ^2 to be less than (1-), or equivalently we require the ratio of (1-) to ^2 to be greater than 1. It works out that the solution a is the product of the mean and the amount by which the ratio of (1-) to ^2 exceeds 1.
VerificationHere is a little code to check for errors in the derivation above. It generates and ^2 values at random, solves for a and b, then checks that the beta(a, b) distribution has the specified mean and variance.
from scipy.stats import uniform, beta for _ in range(100): mu = uniform.rvs() sigma2 = uniform.rvs(0, mu*(1-mu)) a = mu*(mu*(1-mu)/sigma2 - 1) b = a*(1-mu)/mu x = beta(a, b) assert( abs(x.mean() - mu) < 1e-10) assert( abs(x.var() - sigma2) < 1e-10) print("Done")Related posts- Determining a distribution from two quantiles
- Error in the normal approximation to a beta
- Diagram of probability distribution relationships
[1] It's often easiest to think of probability densities ignoring proportionality constants. Densities integrate to 1, so the proportionality constants are determined by the rest of the expression for the density. In the case of the beta distribution, the proportionality constant works out to (a + b) / (a) (b).
[2] The variance of a beta distribution factors into (1-)/(a + b + 1), so it is less than (1-).
The post Beta distribution with given mean and variance first appeared on John D. Cook.