Supercomputing Heat Transfer between 2D Electronic Components
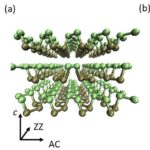
Researchers are using XSEDE supercomputing resources in the search for new materials for power-efficient electronics. "Using a combination of calculations on XSEDE-allocated resources and lab experiments, a UCLA-led group showed that an atomistic model can explain and predict the transfer of heat between aluminum and black phosphorous, a highly anisotropic material with possible applications in future devices."
The post Supercomputing Heat Transfer between 2D Electronic Components appeared first on insideHPC.