Creators of modern rechargeable batteries share Nobel prize
If you had to slip a couple AAs into your smartphone every morning to check your email, browse Instagram, and text your friends, chances are the mobile revolution would not have been quite so revolutionary. Fortunately the rechargeable lithium-ion battery was invented - a decades-long task for which three men have just been awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
The prize this year honors M. Stanley Whittingham, John Goodenough, and Akira Yoshino, all of whom contributed to the development of what is today the most common form of portable power. Without them (and of course those they worked with, and those who came before) we would be tied to even more wasteful and/or stationary sources of energy.
Lead-acid batteries had been in use for nearly a century by the time people really got to thinking about taking things to the next level with lithium, a lightweight metal with desirable electrical properties. But lithium is also highly reactive with air and water, making finding suitable substances to pair it with difficult.
Experiments in the '50s and '60s laid the groundwork for more targeted investigations, in particular Whittingham's. He and partner Fred Gamble showed in 1976 that lithium ions, after donating electrons to produce a charge, fit perfectly into a lattice of titanium disulfide - where they sit patiently (in their "van der Waals gaps") until an electron is provided during recharging. Unfortunately this design also used a lithium anode that could be highly reactive (think fire) if bent or crushed.
John Goodenough and his team soon developed a better cathode material (where the lithium ions rested) with a much higher potential - more power could be drawn, opening new possibilities for applications. This, combined with the fact that the metallic lithium anodes could be highly reactive (think fire) if bent or crushed, led to increased research on making batteries safe as well as useful.
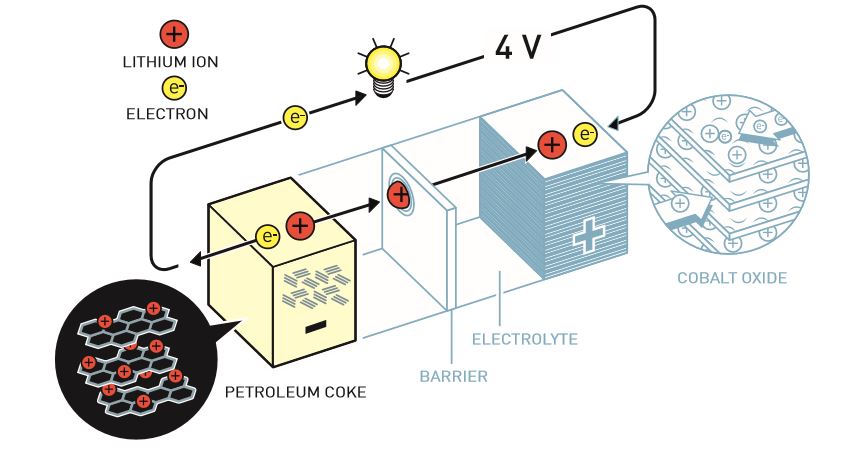
In 1985 research by Akira Yoshino led to the discovery of several materials (whose names won't mean anything to anyone without domain knowledge) that could perform as well while also being able to be physically damaged and not cause any major trouble.
Many, many improvements have been made since then, but the essentials of the technology were laid out by these teams. And soon after lithium-ion batteries were shown to be safe, capacious, and able to be recharged hundreds of times, they were found in laptops, medical devices, and eventually mobile phones. Today, after three more decades of enhancements, lithium batteries are now taking on gasoline as the energy storage medium of choice for human transportation.
The three scholars whose work most powerfully advanced this technology from theory to commercial reality were awarded equal shares of this year's Nobel Prize in Chemistry, each taking home a third of the million and, more importantly, the distinction of being recognized in historic fashion.