Nooks set to seed its own in the world of virtual HQs
After operating in beta for a year, Nooks, a virtual workspace space targeting distributed teams, has attracted thousands of users and millions of dollars in venture capital. The Stanford student-led upstart has raised a $5 million seed round led by Tola Capital, with participation from Floodgate and investors such as Julia and Kevin Hartz (CEO and chairman of Eventbrite, respectively) and Julia Lipton, the founder of Awesome People Ventures.
The financing signals yet another cadre of investors betting on a company within the world of virtual HQs, a cohort that includes dozens of startups that believe distributed employees are ready to graduate from Zoom and into metaverses" built with productivity and gamification in mind. This is Kevin Hartz's second investment in a virtual HQ, with his first in Gather. As of today, Sequoia Capital, Andreessen Horowitz, Menlo, Battery Ventures, Index Ventures, Y Combinator, Homebrew and Floodgate all have stakes in different virtual HQ startups.
In other words: Even with investors pouring money in, Nooks has its work cut out for it.
Nooks was launched in May 2020 by Stanford students Daniel Lee, Rohan Suri, Nikhil Cheerla, and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute's Andrew Qu. Like nearly every other person unexpectedly flung into the world of remote work, the trio experienced Zoom fatigue through school and classes. They soon saw a necessity to build a space for higher-performing teams and like-minded communities to enjoy working together.
The co-founders first piloted Nooks within Stanford, giving it to teaching assistants to use as an engaging layer to summer virtual classes. The initial use case for Nooks looked like office hours, and homework parties, says Lee. Since initially piloting in schools, Nooks has grown to focus more on helping distributed teams work, but the ethos has stayed consistent.
There should be this persistent space where, instead of just being in an ephemeral space like a meeting, you can go somewhere to create more spontaneous connections," Lee said.
Nooks' hooksWhen a user enters Nooks, they are greeted by a Slack-like interface. Instead of a panel of channels on the left, though, employees are invited to enter spaces." Each space can vary in purpose, from a front-desk mock-up to a beach hangout or a design huddle. Nooks has a space dedicated to bashing bugs that show up in code. Upon first entry into the platform, the Nooks UX stood out as different from some of its competitors. While companies like Branch and Gather look like video games with a productivity element, Nooks skips the avatar feel altogether, looking closer to Teamflow or Tandem. The company uses a video API to let each person take up little orbs of space, and adds integrations of platforms like Google Docs, YouTube, Asana or GitHub.
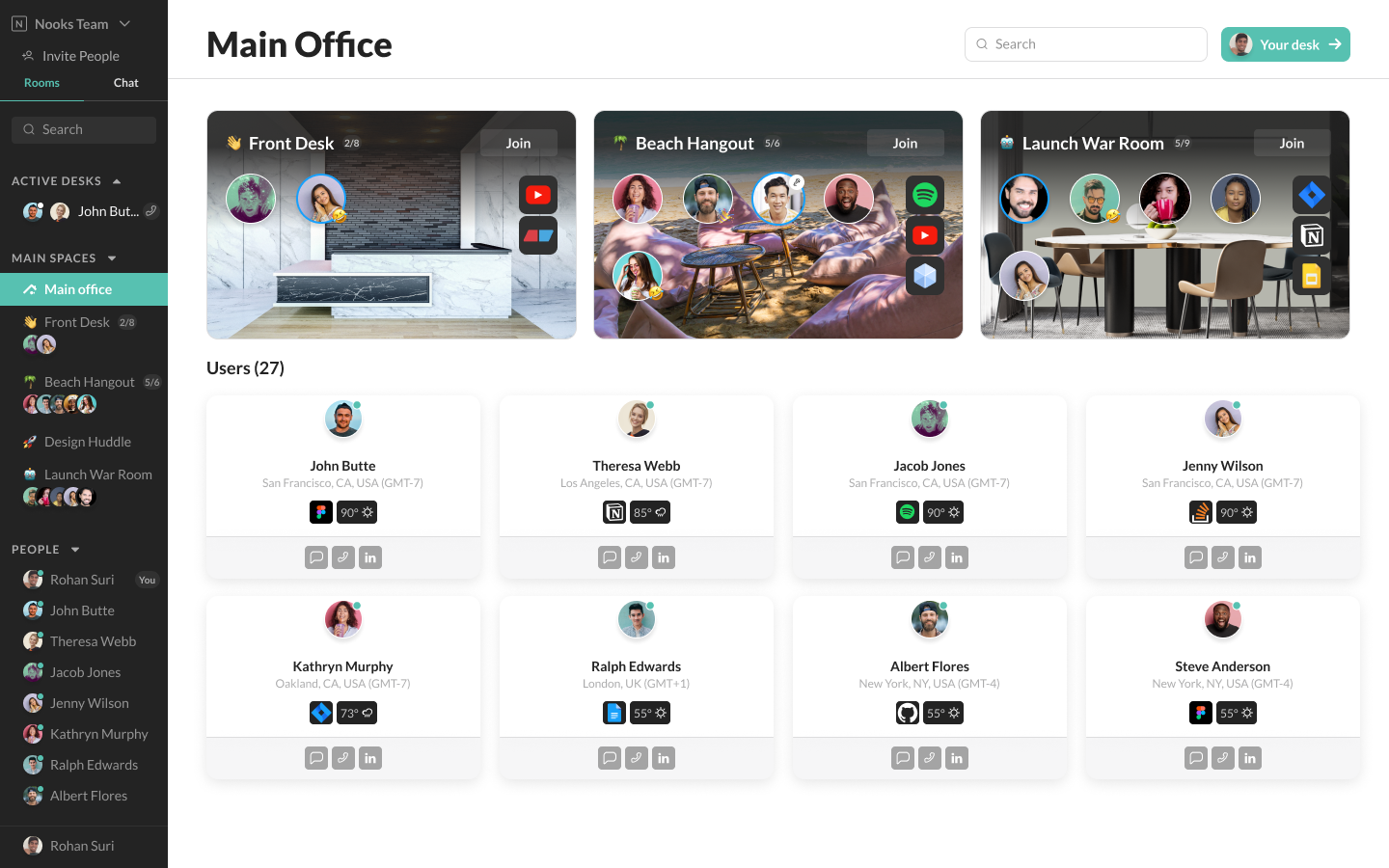
Image Credits: Nooks
Co-founder Suri said that the company decided to go for a simpler aesthetic to promote conversation, not more clicking.
We don't actually believe that in order to talk to someone you need to be a video gamer, have your avatar around and go walk up to them," he said. It should be as simple as seeing them in a room, and entering that room."
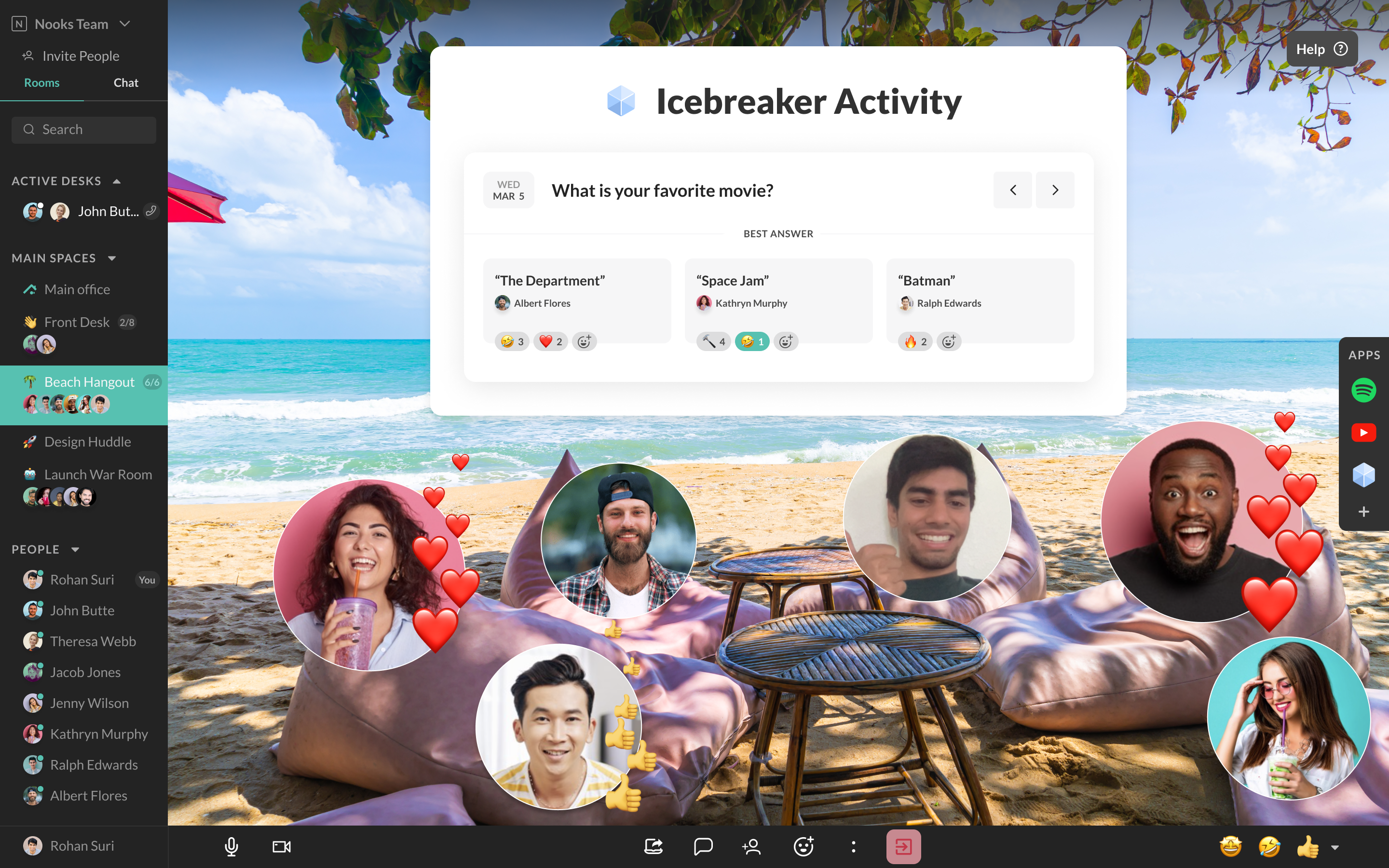
Image Credits: Nooks
Of course, the company is working to balance that simplicity with an engaging environment, and includes customization of spaces and background music. There's a whisper feature" that allows peers to talk to each other during a presentation, virtual sales floors where Nooks creates leaderboards of top sellers and co-working spaces to promote cross-pollination of ideas.
Simplicity can come at the cost of spontaneity. While other virtual HQ platforms use spatial audio to create the feeling of a bump in" - voices get louder when you are near other co-workers and quieter when you toggle away - Lee said that Nooks promotes impromptu collaboration and casual conversations by always making it so that there's only one click to talk to anyone."
While frictionless communication is an important feature, it can't be Nooks' only hook. Platforms like Slack, Hangouts and even Twitter DMs only require one click (max two!) for a user to communicate with someone. Not to mention that Slack is releasing a series of communication tools around spontaneity and live communication.
Still, Nooks currently has thousands of weekly active users from teams and organizations like Stanford, Embroker and Workato. Teams using Nooks spend an average of six hours a day on the platform, the company said.
Hybrid work's virtual growing pains
As the pandemic fades in parts of the world, startups like Nooks will need to figure out ways to adapt to the return of hybrid teams after a long stint of mostly remote work. The new challenge for these startups is how they position themselves to embed well into the new culture of work.
And proximity bias might make that hard to do.
Proximity bias is the idea that employees who go in-person are valued higher than employees who work virtually. It's one of the realities that make hybrid work so hard to pull off at scale: Equity suffers when a group of employees is positioned as more important or prized only because they can travel to an office.
Virtual workspace startups, especially the ones that want to bring work culture online, could accidentally overly fragment those who work from home versus those who work in-person. The fragmentation will disproportionately impact historically overlooked individuals, which include minorities and women. Notably, of the virtual HQs out there, most have been built, run and funded by men.
When asked about how they are combating proximity bias, Lee said that more frequent, fluid and casual conversation with remote employees helps them build stronger bonds with the rest of the team." Sure enough, there's an argument that many virtual HQ startups launched to extinguish proximity bias by bringing everyone in an office to the same digital world.
Ultimately, equalizing the playing field will require aggressive intention. How can a startup make sure virtual HQ employees have access to a spontaneous, in-person stand-up in Conference Room A? How does a platform give any employee, regardless of location, the chance to give input, disagree or share post-meeting banter? Can avatars, or floating video orbs, start to give subtle physical cues beyond a clap or thumbs up?
I'd wager that these features are the moonshot, and survival hack, for virtual HQ startups long-term.