Tickle Pill Bug Toes With These Haptic Microfingers
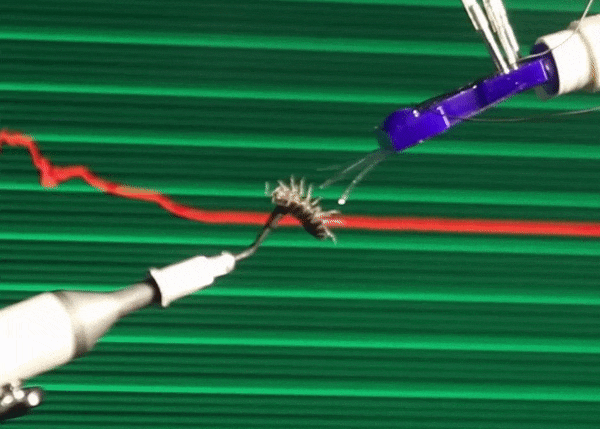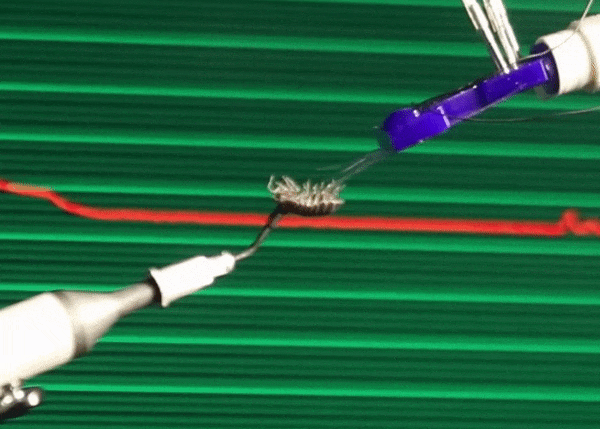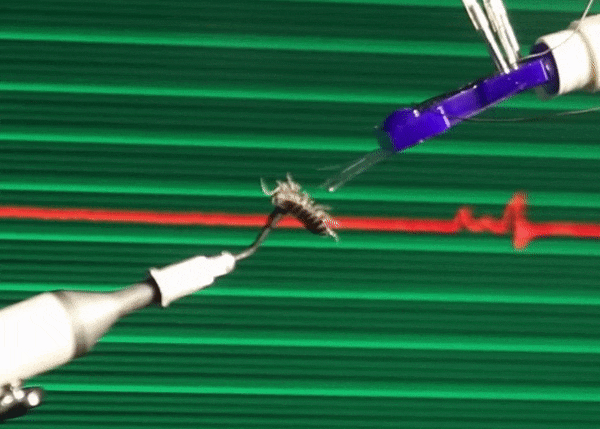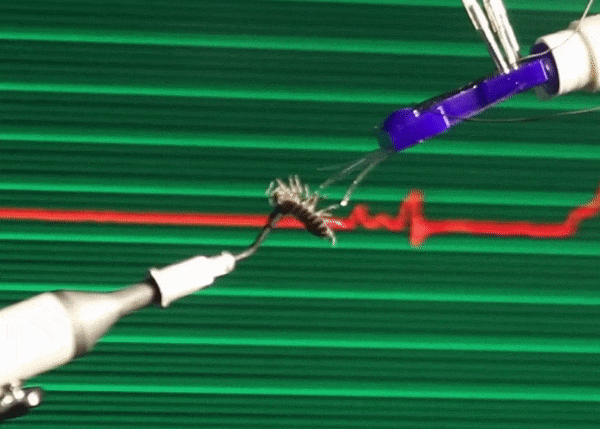
All things considered, we humans are kind of big, which is very limiting to how we can comfortably interact with the world. The practical effect of this is that we tend to prioritize things that we can see and touch and otherwise directly experience, even if those things are only a small part of the world in which we live. A recent study conservatively estimates that there are 2.5 million ants for every one human on Earth. And that's just ants. There are probably something like 7 million different species of terrestrial insects, and humans have only even noticed like 10 percent of them. The result of this disconnect is that when (for example) insect populations around the world start to crater, it takes us much longer to first notice, care, and act.
To give the small scale the attention that it deserves, we need a way of interacting with it. In a paper recently published in Scientific Reports, roboticists from Ritsumeikan University in Japan demonstrate a haptic teleoperation system that connects a human hand on one end with microfingers on the other, letting the user feel what it's like to give a pill bug a tummy rub.
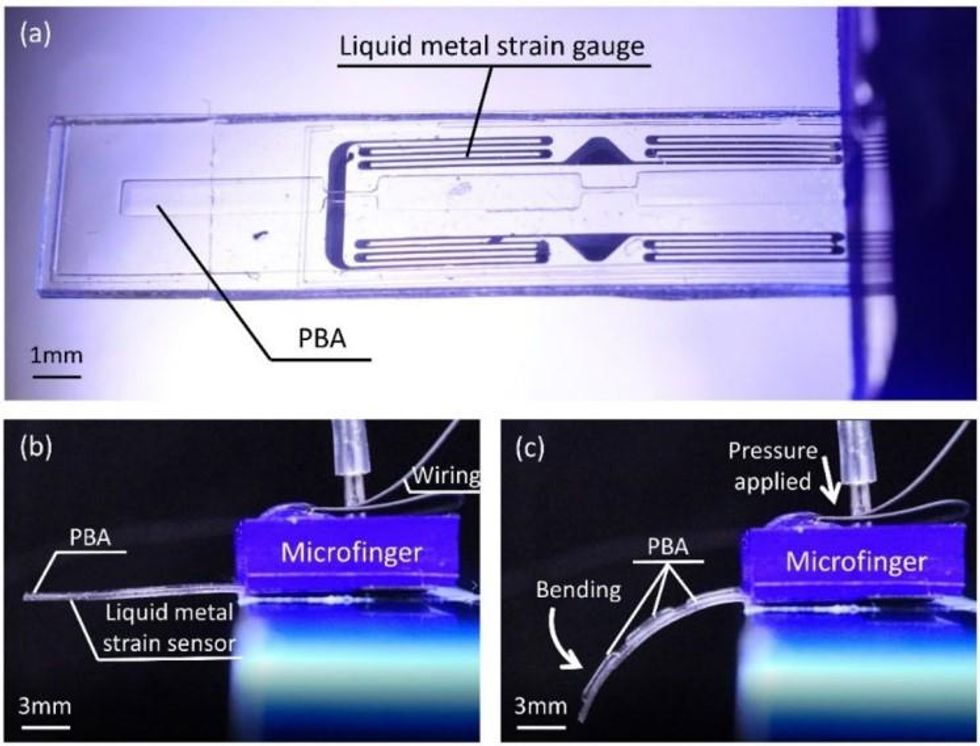 At top, a microfinger showing the pneumatic balloon actuator (PBA) and liquid metal strain gauge. At bottom left, when the PBA is deflated, the microfinger is straight. At bottom right, inflating the PBA causes the finger to bend downwards.
At top, a microfinger showing the pneumatic balloon actuator (PBA) and liquid metal strain gauge. At bottom left, when the PBA is deflated, the microfinger is straight. At bottom right, inflating the PBA causes the finger to bend downwards.
These microfingers are just 12 millimeters long, 3 mm wide, and 490 microns (m) thick. Inside of each microfinger is a pneumatic balloon actuator, which is just a hollow channel that can be pressurized with air. Since the channel is on the top of the microfinger, when the channel is inflated, it bulges upward, causing the microfinger to bend down. When pressure is reduced, the microfinger returns to its original position. Separate channels in the microfinger are filled with liquid metal, and as the microfinger bends, the channels elongate, thinning out the metal. By measuring the resistance of the metal, you can tell how much the finger is being bent. This combination of actuation and force sensing means that a human-size haptic system can be used as a force feedback interface: As you move your fingers, the microfingers will move, and forces can be transmitted back to you, allowing you to feel what the microfingers feel.
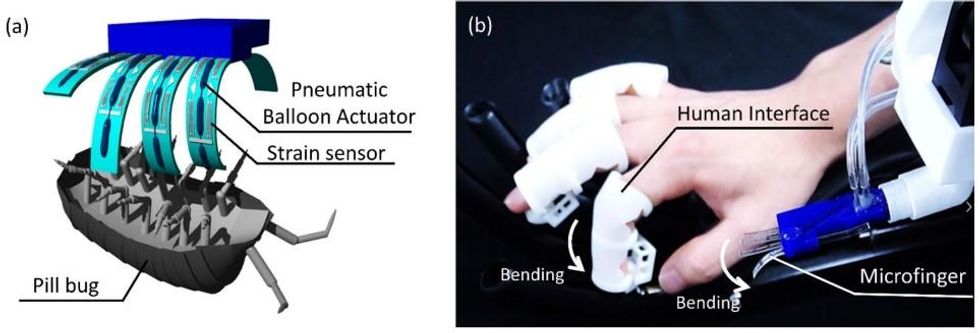 The microfingers (left) can be connected to a haptic feedback and control system for use by a human.
The microfingers (left) can be connected to a haptic feedback and control system for use by a human.
Fans of the golden age of science fiction will recognize this system as a version of Waldo F. Jones' Synchronous Reduplicating Pantograph, although the concept has even deeper roots in sci-fi:
The thought suddenly struck me: I can make micro hands for my little hands. I can make the same gloves for them as I did for my living hands, use the same system to connect them to the handles ten times smaller than my micro arms, and then ... I will have real micro arms, they will chop my movements two hundred times. With these hands I will burst into such a smallness of life that they have only seen, but where no one else has disposed of their own hands. And I got to work.
With their very real and not science fiction system, the researchers were able to successfully determine that pill bugs can exert about 10 micro-Newtons of force through their legs, which is about the same as what has been estimated using other techniques. This is just a proof of concept study, but I'm excited about the potential here, because there is still so much of the world that humans haven't yet been able to really touch. And besides just insect-scale tickling, there's a broader practical context here around the development of insect-scale robots. Insects have had insect-scale sensing and mobility and whatnot pretty well figured out for a long time now, and if we're going to make robots that can do insect-like things, we're going to do it by learning as much as we can directly from insects themselves.
With our strain-sensing microfinger, we were able to directly measure the pushing motion and force of the legs and torso of a pill bug-something that has been impossible to achieve previously. We anticipate that our results will lead to further technological development for microfinger-insect interactions, leading to human-environment interactions at much smaller scales."
-Satoshi Konishi, Ritsumeikan University