Framework for building bio-bots
by noreply@blogger.com (brian wang) from NextBigFuture.com on (#2D8VP)
For the past several years, researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have been developing a class of walking "bio-bots" powered by muscle cells and controlled with electrical and optical pulses. Now, Bioengineering Professor Rashid Bashir's research group is sharing the recipe for the current generation of bio-bots. Their how-to paper is the cover article in Nature Protocols.
"The protocol teaches every step of building a bio-bot, from 3D printing the skeleton to tissue engineering the skeletal muscle actuator, including manufacturers and part numbers for every single thing we use in the lab," explained Ritu Raman, now a postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Bioengineering and first author of the paper
"This protocol is essentially intended to be a one-stop reference for any scientist around the world who wants to replicate the results we showed in our PNAS 2016 and PNAS 2014 papers, and give them a framework for building their own bio-bots for a variety of applications," Raman said.
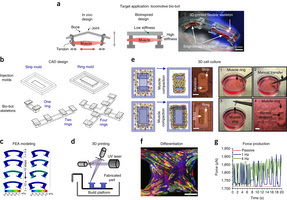 Bio-bot design process overview.
Bio-bot design process overview.
Nature Protocols - A modular approach to the design, fabrication, and characterization of muscle-powered biological machines
Read more










"The protocol teaches every step of building a bio-bot, from 3D printing the skeleton to tissue engineering the skeletal muscle actuator, including manufacturers and part numbers for every single thing we use in the lab," explained Ritu Raman, now a postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Bioengineering and first author of the paper
"This protocol is essentially intended to be a one-stop reference for any scientist around the world who wants to replicate the results we showed in our PNAS 2016 and PNAS 2014 papers, and give them a framework for building their own bio-bots for a variety of applications," Raman said.
 Bio-bot design process overview.
Bio-bot design process overview.Nature Protocols - A modular approach to the design, fabrication, and characterization of muscle-powered biological machines
Read more