Nanostructured electrode could boost lithium battery storage by 50%
by noreply@blogger.com (brian wang) from NextBigFuture.com on (#2DCCX)
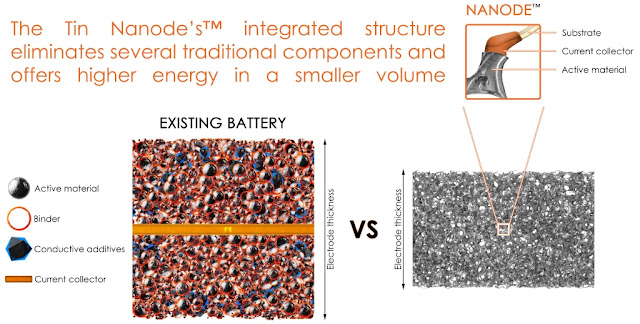
The Nanodea is a three-dimensional, nano-structured, porous electrode that will overcome the limitations of today's batteries by storing as much as 50% more energy than existing technologies. This allows the batteries to last longer between charges while also charging faster. These achievements are due to both the material structure and the use of tin as the active material. Tin is known to have much higher energy density than the current graphite technology, but until now its commercial success has been limited due to its tendency to swell during charging, causing stress in the electrode material and leading to a rapid loss in energy. Current commercial lithium ion batteries employ a foil/particle system as the electrode structure. The capability of such electrodes to deal with volume expansion of high energy materials is limited, because as the particles swell, the electrode expands.
The Tin Nanode'sa integrated electrode structure contributes to the relaxation of stress associated with electrode materials undergoing high volume expansion. This is possible because thin films of active material are spread over a 3D and porous network of fibres, rather than stacking particles on a flat copper foil. This enables the electrode structure to deal with the volume expansion of the tin while retaining dimensional stability at the electrode level.
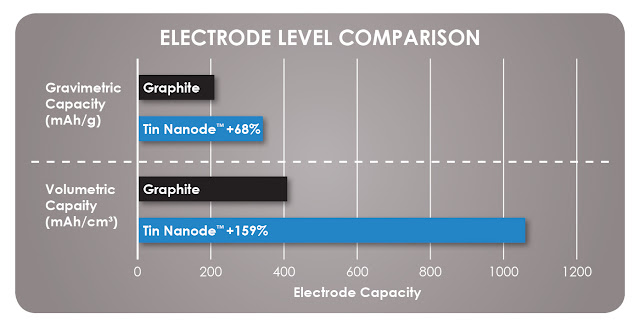
The major advantage of the Tin Nanodea is its capacity to store the same amount of energy in a smaller volume, compared to commercial lithium ion batteries. This translates into a reduction in volume and cost of the overall battery.
Read more










The Tin Nanode'sa integrated electrode structure contributes to the relaxation of stress associated with electrode materials undergoing high volume expansion. This is possible because thin films of active material are spread over a 3D and porous network of fibres, rather than stacking particles on a flat copper foil. This enables the electrode structure to deal with the volume expansion of the tin while retaining dimensional stability at the electrode level.
The major advantage of the Tin Nanodea is its capacity to store the same amount of energy in a smaller volume, compared to commercial lithium ion batteries. This translates into a reduction in volume and cost of the overall battery.


Read more