Quantum Learning
by noreply@blogger.com (brian wang) from NextBigFuture.com on (#2FSA4)
The efficient characterization of quantum systems, the verification of the operations of quantum devices and the validation of underpinning physical models are central challenges for quantum technologies and fundamental physics. The computational cost of such studies could be improved by machine learning enhanced by quantum simulators. Here researchers interface two different quantum systems through a classical channel-a silicon-photonics quantum simulator and an electron spin in a diamond nitrogen-vacancy centre-and use the former to learn the Hamiltonian of the latter via Bayesian inference. Researchers learn the salient Hamiltonian parameter with an uncertainty of approximately. Furthermore, an observed saturation in the learning algorithm suggests deficiencies in the underlying Hamiltonian model, which we exploit to further improve the model. They implement an interactive version of the protocol and experimentally show its ability to characterize the operation of the quantum photonic device.
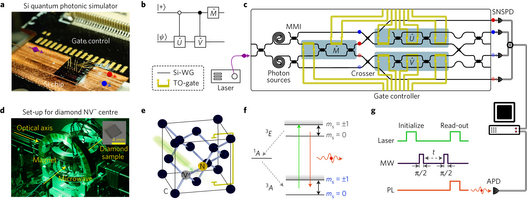 Quantum photonic simulator and diamond nitrogen-vacancy centre
Quantum photonic simulator and diamond nitrogen-vacancy centre
Nature Physics - Experimental quantum Hamiltonian learning
Read more










 Quantum photonic simulator and diamond nitrogen-vacancy centre
Quantum photonic simulator and diamond nitrogen-vacancy centreNature Physics - Experimental quantum Hamiltonian learning
Read more