 |
by Darian Woods on (#6WTDA)
President Donald Trump has been loudly critical of Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell for years now. Since January, the President has accused him of playing politics by keeping interest rates high. Trump has also threatened to oust Powell - which would mark an extraordinary shift away from the independence of the central bank.Today on the show, three Indicators: a short history of the Federal Reserve and why it's insulated from day-to-day politics; how the Fed amassed a ton of power in recent years; and a Trump executive order that took some of that power away.The original episodes from the Indicator were produced by Corey Bridges, Brittany Cronin, and Julia Ritchey. They were engineered by Cena Loffredo, James Willetts, and Gilly Moon, and fact-checked by Sierra Juarez. Kate Concannon is the editor of the Indicator. Follow us wherever you get your podcasts.This episode of Planet Money was produced by James Sneed and edited by Marianne McCune & Mary Childs. Alex Goldmark is our executive producer.For more of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Or, find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.
|
 NPR: Planet Money
NPR: Planet Money
| Link | https://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=93559255 |
| Feed | http://www.npr.org/rss/rss.php?id=93559255 |
| Copyright | Copyright 2024 NPR - For Personal Use Only |
| Updated | 2026-01-26 21:01 |
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6WT28)
Donald Trump grew up learning to make deals. He's also loved tariffs since the 1970s. So are his market-shaking tariffs a bargaining chip? Or are they here permanently? We go all the way back to Trump's childhood to try to figure out if Dealmaker Don or Tariff Man Trump is in charge. Marc Fisher's book with Michael Kranish is Trump, Revealed. Related episodes: What's so bad about a trade deficit? (Apple / Spotify) Why there's no referee for the trade war (Apple / Spotify) Tariffied! We check in on businesses (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Tyler Jones. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Adrian Ma on (#6WS94)
By now, you've heard a lot about how the U.S.-China trade war is affecting American consumers, businesses and the stock market. But how is the trade war being felt in China? Today on the show, two of NPR's in-house China experts, Emily Feng and John Ruwitch, explain the view from China. Related episodes: What might save China's economy (Apple / Spotify) Tarrified! We check in on businesses (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Wailin Wong on (#6WRNE)
It's time for The Indicator Quiz! We test you, dear listener, on your knowledge of topics that we've covered on The Indicator.Today's quiz show involves a DJ from Vancouver, Washington that tests his economic education on the World Trade Organization, the Panama Canal, and of course, Bad Bunny. Play along with us and see how you do!Are you interested in being a contestant on our next Indicator Quiz? Email us your name and phone number at indicator@npr.org and put "Indicator Quiz" in the subject line.Related episodes:WWE, a very expensive banana, and a quiz contestant (Apple / Spotify)For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.
|
 |
by Kenny Malone on (#6WQM2)
Recently, one of our NPR colleagues wrote a message to all of NPR saying he had extra eggs to sell for cheap, but needed a fair way to distribute them during a shortage. What is Planet Money here for if not to get OVERLY involved in this kind of situation?Our colleague didn't want to charge more than $5, so we couldn't just auction the eggs off. A lottery? Too boring, he said. Okay! A very Planet Money puzzle to solve.Today on the show, we go in search of novel systems to help our colleague decide who gets his scarce resource: cheap, farm-fresh eggs. We steal from the world of new product development to try and secretly test for egg love, and we discover a pricing method used in development economics that may be America's next great gameshow.This episode of Planet Money was produced by Emma Peaslee and it was edited by Marianne McCune. It was fact checked by Sierra Juarez and engineered by Jimmy Keeley. Alex Goldmark is our executive producer.Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.Music: NPR Source Audio - "Punchy Punchline," "Game Face," "Feeling the Funk," and "The Host Most Wanted"
|
by Willa Rubin on (#6WPB9)
American winemakers tell us why tariffs hurt their industry.
 |
by Wailin Wong on (#6WP8M)
The current economic upheaval has lots of us scrambling for our glossaries and history books. Today on the show, the editor-in-chief of Investopedia walks us through three vocab terms - spanning topics from tariff history to market volatility - that are spiking on the website lately. Related listening:Did Trump enable insider trading? (Apple / Spotify)What's a moneyline bet anyway? (Apple / Spotify)Why tariffs are SO back (Apple / Spotify)For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Keith Romer on (#6WNC1)
OIRA - the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs - is an obscure, but powerful federal office around the corner from the White House. President Trump has decided that it should get even more powerful.For the last 45 years, OIRA has overseen most federal agencies by reviewing proposed regulations to make sure they agree with the President's policies and don't conflict with the work of other agencies. But one set of federal agencies has always been exempt from this review process - independent federal agencies like the SEC, FTC, FCC, and Federal Reserve. Until now.According to a new executive order, those independent agencies are about to get a lot less independent. We take a look at what this change could mean for financial markets...and the future of American democracy.This episode was produced by James Sneed and Willa Rubin. It was edited by Jess Jiang and engineered by Jimmy Keeley. It was fact-checked by Sierra Juarez. Alex Goldmark is our executive producer.Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.Music: Universal Music Production - "Tanga," "The Jump Back," and "Kumbatia."
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6WNC2)
On the morning of April 9, President Trump posted on Truth Social "THIS IS A GREAT TIME TO BUY!!! DJT." Around four hours later, he announced a pause on some new tariffs, causing a stock market spike. Now, Democrats are demanding an investigation into possible insider trading. But were Trump's posts actually insider trading?Related episodes:Morally questionable, economically efficient (Apple / Spotify) An insider trader tells all For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Paddy Hirsch on (#6WMGP)
If you've ever passed through airport customs overseas and been refunded a VAT - or value added tax - for souvenirs, you've benefited from the VAT system. But President Trump says VAT is unfair to the U.S. On today's episode, we learn what VAT is and what it isn't. Related episodes:What's so bad about a trade deficit? (Apple / Spotify)Tarrified! We check in on businesses (Apple / Spotify)Why there's no referee for the trade war (Apple / Spotify)For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Wailin Wong on (#6WKQH)
The federal government has been tracking the weather for more than 150 years. But the rise of the Internet and big tech have made weather forecasting a more crowded space. Today on the show, the value of an accurate forecast and how the Trump administration's early moves are clouding the government's future forecasting. This piece originally aired in November 2024. Related stories: Hazard maps: The curse of knowledge (Apple / Spotify) Should we invest more in weather forecasting? After a year of deadly weather, cities look to private forecasters to save lives Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Amanda Aronczyk on (#6WJQ9)
How do you run a business when a trade war is brewing? As President Trump's tariffs kick in - or are paused or are restarted - businesses around the world are trying to navigate the uncertainty.And, while trade is this big global thing, it is made up of individual farmers and business owners and truckers and manufacturers. Millions of people all over the world are being forced to reevaluate relationships that they've been building for years. Canadians have had a head start - Trump announced his plan to tariff Canadian goods on day one in office. So in today's episode: how one Canadian small business is trying to manage the chaos.This episode was produced by Sylvie Douglis and edited by Sally Helm. It was engineered by Cena Loffredo and fact-checked by Sierra Juarez. Alex Goldmark is our executive producer. Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.Music: NPR Source Audio - "Mr. Chill," "Lazy Ranger," and "Guess What"
|
 |
by Greg Rosalsky on (#6WJGX)
It's not just tariffs. The White House is rethinking the central role of the dollar in the global economy.
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6WJ2W)
Today on the show, we discuss why the IRS is sharing some taxpayer information, why bonds and stocks both fell, and how robots will replace you,or at least most of your chore wheel, in the near future.Related episodes: Why are stocks and bonds both falling? For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Wailin Wong on (#6WH79)
"There's no bad weather, only bad clothing." That's the motto of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, where Austan Goolsbee is president. As economic weather conditions stay unpredictable, Austan tells us how he's gearing up for tariffs, inflation, and more. Related episodes:The Fed cut rates ... now what? (featuring: Sasquatch) (Apple / Spotify)Tariffied! We check in on businesses (Apple / Spotify)A chat with the president of the San Francisco Fed (Apple / Spotify)Is the economy going stag(flation)?For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Mary Childs on (#6WH00)
At the heart of President Trump's tariffs is this idea that we should not be buying more from other countries than they are buying from us. Basically, he wants to get rid of the trade deficit. And in the wake of the tariff announcement we got a LOT of questions from listeners about what that means. Do trade deficits matter? Is it bad to have a trade deficit? Are we getting ripped off? Today on the show - we tackle those questions. This episode of Planet Money was produced by Emma Peaslee and edited by Marianne McCune and Kenny Malone. It was fact checked by Sarah McClure and engineered by Kwesi Lee. Alex Goldmark is our executive producer. Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.Music: NPR Source Audio - "The Westerners," "Liquid Courage," and "Blazed and Emboldened"
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6WGBD)
Today on the show, we meet Canada's new Prime Minister, economist Mark Carney. What's it like when your former job - being a non-political banker who decides a country's interest rate - bleeds into your now-political decisions on everything?Related episodes: A polite message from Canada to the U.S. (Apple / Spotify)
|
 |
by Wailin Wong on (#6WFG0)
President Trump claims a main goal of his crippling tariffs is to address the U.S. trade deficit. So is the U.S. trade deficit a problem? On today's show, why we'll never have a trade surplus with every single country; what the benefits of a trade deficit are; and whether or not the trade deficit affects jobs. Related episodes:Tariffied! We check in on businesses (Apple / Spotify) Why there's no referee for the trade war (Apple / Spotify) Common economic myths debunked (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
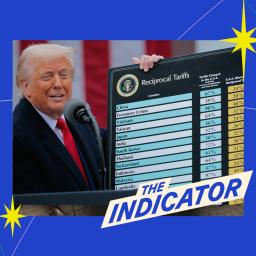 |
by Darian Woods on (#6WEP3)
Trump's wave of tariffs is here. Just about everyone in the world of business is still processing exactly what this means. It's a massive, widespread increase in taxes. Today on the show, we hear from business people we've had on the show who tell us what they're doing in response to the latest, and largest, wave of tariffs. Related episodes: Trump's contradictory trade policies (Apple / Spotify) How's ... everybody doing? (Apple / Spotify) How Shein became a fast-fashion behemoth (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Erika Beras on (#6WDPP)
Ever wondered why you can buy fresh Peruvian blueberries in the dead of winter? The answer, surprisingly, is tied to cocaine. Today on the show, we look at how the war on drugs led to an American trade policy and a foreign aid initiative that won us blueberries all year round. And for more on trade and tariffs check out Planet Money's homepage. We've got articles looking at how much the new tariffs will raise prices and shows on everything from diamonds to potatoes to why you bought your couch. This episode was produced by Sylvie Douglis with help from Willa Rubin. It was edited by Marianne McCune and engineered by Jimmy Keeley. It was fact-checked by Sierra Juarez. Alex Goldmark is our executive producer.Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.Music: Source Audio: "Martini Shaker," "You the Man," and "Leisure Girls."
|
 |
by Wailin Wong on (#6WDEG)
It's Jobs Friday and all eyes are on government workers. Will the Trump administration's layoffs finally show up in the latest jobs report? Today on the show, we look at the numbers for federal workers and who's trying to hire them. Related listening: Can ... we still trust the monthly jobs report (Apple / Spotify) The last time we shrank the federal workforce (Apple / Spotify) A 'Fork in the Road' for federal employees (Apple / Spotify) How local government is propping up the U.S. labor market For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Jeff Guo on (#6WDBA)
The administration revealed how they calculated the tariffs. Buried in that math is a straightforward answer to a question Trump has long refused to answer: How much will his tariffs raise prices?
|
 |
by Justin Barney on (#6WC7V)
There have now been a few major vinyl booms. And unbeknownst to many, a small village in the Czech Republic has been responsible for manufacturing a large number of these albums. On today's show, how this dominant player became a problem for its competitors in the U.S. Related episodes: Rumor has it Adele broke the vinyl supply chain 'Let's Get It On' ... in court (Update) (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Mary Childs on (#6WC1Q)
What are tariffs good for?For years, mainstream economists have basically said: tariffs are not good. They are an import tax paid by consumers, they've said, and they discourage free trade, and we want more! Because free trade has broadly led to more global economic growth.But global trade hasn't been all positive for Americans, and in the worldview of President Trump's administration, tariffs can be used to right some of those wrongs. And the U.S. has economic leverage. So if the U.S. wants to level the playing field, it should use that leverage, and use tariffs to accomplish its policy goals.Today on the show: the case for tariffs. We talk to a lonely economist who's been sounding the alarm for years that more and free-er trade isn't always better. And we speak to economists in President Trump's orbit who make the case for how tariffs can be a potent economic and political tool.This episode was produced by Willa Rubin and edited by Meg Cramer. It was fact-checked by Sarah McClure and engineered by James Willetts. Alex Goldmark is our executive producer. Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.Music: Universal Music Production: "Funky Reverie" and "With It;" Audio Network: "Slush Puppy Soul."
|
 |
by Stephan Bisaha on (#6WBCA)
Billions of tech dollars flowing into a community to build data centers should transform a local economy ... right? Well, maybe not. On today's episode: Why data centers create few permanent jobs. And why communities might want them anyway.Related episodes:Why China's DeepSeek AI is such a big deal (Apple / Spotify)Is AI overrated? (Apple / Spotify)For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Greg Rosalsky on (#6WAMQ)
A controversial study raised the specter that Girl Scout cookies are unsafe. Authorities say they are safe, but the whole saga highlights a breakdown of trust in American institutions.
|
 |
by Sierra Juarez on (#6WAH2)
Mexico is gearing up to directly elect federal and state judges for the first time this June. President Claudia Sheinbaum says the new system will combat nepotism and increase the integrity of the courts. But critics see it as a naked attempt to dilute the court's independence. Today on the show, how Mexico's judicial reforms are creating angst for businesses at home and abroad. Related episodes: SCOTUS: De-facto pro-business? For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Cooper Katz-McKim. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6W9NG)
Brands trying to be your best bud. Generational labels. Gendered double standards. Today on the show: three advertising experts bring their three pet peeves in advertisements.Related episodes: How to make an ad memorable (Apple / Spotify) J. ScrewedThe Gender Gap Series: The Problem With The Pink TaxFor sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Jeff Guo on (#6W8GK)
Earth can sustain life for another 100 million years, but can we? This episode, we partner with Radiolab to take stock of the essential raw materials that enable us to live as we do here on Earth - everything from sand to copper to oil - and tally up how much we have left. Are we living with reckless abandon? And if so, is there even a way to stop? A simultaneously terrifying and delightful conversation about bird poop, daredevil drivers, and some staggering back-of-the-envelope math. Radiolab's original episode was produced and edited by Pat Walters and Soren Wheeler. Fact-checking by Natalie Middleton. The Planet Money edition of this episode was produced by Emma Peaslee and edited by Alex Goldmark and Jess Jiang. Special thanks to Jennifer Brandel.Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.Music: NPR Source Audio - "Wir Rollen"
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6W7WR)
On Indicators of the Week, we look at a huge projected tax shortfall, the price of copper and the afterlife of Napster, the peer-to-peer file-sharing service that refuses to die. Related episodes: A new-ish gold rush and other indicators (Apple / Spotify) Can the Federal Reserve stay independent (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Sean Saldana on (#6W6ZA)
Many nonprofits accept your used cars as a way to donate. This happens from Make-A-Wish America to Habitat for Humanity to ... public radio stations! So, how does the process actually work? And who takes a cut along the way? Today, we follow the car money.Related episodes: Show your love for The Indicator from Planet Money by making a donation For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Jeff Guo on (#6W6H9)
The deal seemed too good to be true. There's a website that's been selling top quality diamonds at bizarrely low prices. Prices we couldn't find at any retail outlet. Prices so low, we could buy a diamond on a public radio budget. So we did. What we got in the mail was a tiny ziploc bag containing a scintillating mystery.On today's show: the Planet Money Diamond (or whatever this sparkly rock turns out to be). We get it analyzed by the experts at the Gemological Institute of America. We investigate where it came from. And, we dive into the economics of glittery stones. Was this a new kind of internet scam? Some supply chain anomaly? Or is something just really weird going on in the world of diamonds?This episode was produced by James Sneed. It was edited by Keith Romer with help from Jess Jiang, fact-checked by Emma Peaslee, and engineered by Kwesi Lee. Alex Goldmark is our executive producer.Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.
|
 |
by Paddy Hirsch on (#6W64D)
As relations between the US and Europe continue to sour, European countries are working to lower their reliance on the U.S. for weapons and security. Today on the show, we ask what Europe needs to do to become independent militarily and what potential barriers could stand in the way.Related episodes:Europe's NATO members take an economic hit (Apple / Spotify)Two Indicators: Economics of the defense industry (Apple / Spotify)For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6W57Y)
What's one word you'd use to describe the 2025 economy? That's the question we fanned out across the U.S. with microphones and open ears. From street parties in the South to an L.A. bookstore to a boardroom in Denver, we listen for financial signals in today's economy. Related episodes: How many times can you say uncertainty in one economic report? (Apple / Spotify) The stock market is down, but you don't need to be (Apple / Spotify) The highs and lows of US rent (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6W4EY)
Half of all workers are showing signs of burnout according to a survey of international workers. Burnout can come from feeling detached from your work's purpose, having too much work, or ... from specialization. Today on the show, we speak with Shigehiro Oishi, author of Life in Three Dimensions: How Curiosity, Exploration, and Experience Make a Fuller, Better Life. Related episodes: Is endless vacation a scam? (Apple / Spotify) Why we work so much For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Nick Fountain on (#6W3H2)
There's one statistic that rules them all when it comes to keeping track of the economy: gross domestic product (GDP). It's the sum of all final transactions, so all the goods or services bought and sold, in an economy. GDP tells us how hot the economy is running, or how cool - like if we might be heading into a recession. And it's an important tool to compare countries, policies, and politicians. It's used by the U.S. government to allocate money and by businesses to make decisions about the future. For close to a century the building blocks of GDP have been the same. Now Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick, has proposed a big change: taking government spending out of GDP. On today's show, can the U.S. change how it measures GDP? We talk with a former head of the BEA - about what he thinks they're likely to do now, and about the pressure he faced while trying to compile GDP for nearly two decades. Turns out, people have always been trying to bend it to make whatever grand project they're working on look better.Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.
|
 |
by Adrian Ma on (#6W2XS)
It's Indicators of the Week! Our weekly look at interesting numbers from the news. On today's show, we welcome back co-host Adrian Ma.We also have the price of gold going up, German defense stocking up, and U.S. mergers and acquisitions slowing down.Related episodes:NPR's Adrian Ma remembers girlfriend, Kiah Duggins, who died in D.C. plane crashEurope's NATO members take an economic hit (Apple / Spotify)For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Paddy Hirsch on (#6W234)
In 2009, Bitcoin launched as the first cryptocurrency. Just under two decades, President Trump has signed an executive order to create the "Strategic Bitcoin Reserve and United States Digital Asset Stockpile." On today's show, we look at what the U.S. government plans for this new strategy, plus who benefits from a crypto reserve.Related episodes:Is an American sovereign wealth fund such a bad idea? (Apple / Spotify)Is 'government crypto' a good idea? (Apple / Spotify)For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Audrey Quinn on (#6W17F)
Note: This original episode ran in 2020.Walter Schramm did everything right as an investor - at least according to the philosophy of Warren Buffett. So how come he lost a small fortune?In this episode, we look into an obscure government program that slurps up forgotten money. We hunt for money we might have left vulnerable and we try to figure out how it got there in the first place so we can tell you where to find the money you've misplaced too.Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.
|
 |
by Wailin Wong on (#6W17E)
Thirty years ago, the U.S. helped create the World Trade Organization, a group of countries linked by a common set of free trade agreements. But then the U.S., starting with the Obama administration, turned against the WTO. This leaves a void where there should be a referee to settle trade disputes between countries. On today's show, how American grievances paralyzed the WTO's dispute settlement system and what happens when the U.S. no longer wants to play by the rules it once agreed to. Related listening: A polite message from Canada to the U.S. (Apple / Spotify)Trump's contradictory trade policies (Apple / Spotify) Worst. Tariffs. Ever. (Update) (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Tyler Jones. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6W0EH)
China has set out its target for economic growth this year: around 5 percent. That's a hefty goal for a nation coming off a painful real estate slump. But leaders have their eyes set on other industries to help its economy grow. Today, we dig into the headwinds and tailwinds facing China's economy. Related episodes: The mess at the heart of China's economy (Apple / Spotify) The race to produce lithium (Apple / Spotify) What's really happening with the Evergrande liquidation (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Greg Rosalsky on (#6W0EJ)
A new study finds that after decades of stagnation, fast-food and other restaurants finally saw a surge in productivity.
|
 |
by Kate Dario on (#6VZGR)
The federal government spends millions of dollars each year on wildlife damage management, a program that includes killing thousands of coyotes. Yet this program may actually have the opposite effect on the coyote's population. Today on the show, why the government keeps spending money on a problem it can't fix. Related episodes: Shooting Bambi to save Mother Nature For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Willa Paskin on (#6VYFQ)
Tupperware is the stealthy star of our modern homes. These plastic storage containers are ubiquitous in our fridges, pantries, and closets. But the original product was revolutionary. So was its breakthrough sales strategy: the Tupperware Party.Led in part by a charismatic housewife turned business innovator, Tupperware pioneered more than the party. Brownie Wise, and the company she came to represent, are behind a core sales technique that we might now recognize as influencer marketing.The company was so successful at its peak, it reached almost cult status. But it didn't last. On our latest episode: Tupperware's success and the company's demise. And how its descendants - in products, and in sales strategies - lived on. This episode is in partnership with Decoder Ring. For even more on the legacy of Tupperware, listen to their full episode. Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6VXSW)
It's Indicators of the Week! Our weekly look at interesting numbers from the news. On today's show, we have Southwest Airlines changing course on their free checked bag policy, skyrocketing fraud, and Americans' insatiable appetite for avocados. Related episodes:More fraud, higher bond yields, and faster airline boardingFor sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Robert Smith on (#6VWVB)
Uncertainty. That's the word-of-the-moment with tariffs, market swings and lots of economic volatility. It's also showing up in the Federal Reserve's latest Beige Book, featuring anecdotes across the U.S. economy. On our latest edition of the Beigies, what can a farmer from the Mississippi Delta tell us about uncertainty? Related episodes: How USAID cuts hurt farmers (Apple / Spotify) Why Trump's potential tariffs are making business owners anxious (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Tyler Jones. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Sarah Gonzalez on (#6VWMA)
If you cut every single federal job President Donald Trump wants to cut, how much money would that save? A president has tried to massively shrink the size of the federal government before. It was in the 90s, under a Democrat.Today on the show: Where they found waste the last time we really looked. (Hint: it wasn't jobs.) And why the pace of firings under Trump might start to slow down.For more:- Lessons for the Future of Government Reform- Is government too big? Reflections on the size and composition of today's federal government- Creating a Government That Works Better and Costs Less This episode of Planet Money was produced by Willa Rubin. It was edited by Jess Jiang and engineered by Jimmy Keeley. We had fact-checking help from Sierra Juarez. Alex Goldmark is our executive producer. Special thanks to Ben Zipperer. Find more Planet Money: Facebook / Instagram / TikTok / Our weekly Newsletter.Listen free at these links: Apple Podcasts, Spotify, the NPR app or anywhere you get podcasts.Help support Planet Money and hear our bonus episodes by subscribing to Planet Money+ in Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org/planetmoney.Music: Audio Network - "West Green Road," "Raise Up," and "Blue and Green."
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6VW0A)
Government cuts. Tariff uncertainty. Sticky interest rates. These are not helping the tumbling stock market. There's a sinking feeling among some Americans that a crash is imminent. But ... should we all be so worried? Today, we brush away the cobwebs of stock market fear and confusion, and bring some long-held facts to the surface. Related episodes: Why to look twice when your portfolio is doing well (Apple / Spotify) The cautionary tale of a recovering day trading addict (Apple / Spotify) For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Tyler Jones. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|
 |
by Paddy Hirsch on (#6VV2R)
The Trump administration has some nits to pick with government spending: They don't think it should be counted as part of the country's GDP, that it should be counted separately. In today's episode, we look at why government spending is part of the U.S.'s GDP and we speculate why Trump's administration might want to take it out ... and what that could mean.
|
 |
by Darian Woods on (#6VT81)
Bad Bunny's new album DeBI TiRAR MaS FOToS laments how Puerto Rico is changing. We look at whether tax breaks to newcomers contributed.Related episodes: The battle for Puerto Rico's beachesWe Set Up An Offshore Company In A Tax Haven For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org. Fact-checking by Sierra Juarez. Music by Drop Electric. Find us: TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, Newsletter.
|